In today’s financial world, understanding your credit score is paramount. Whether you’re applying for a loan, a credit card, or even renting an apartment, your credit score can significantly impact your financial journey. This comprehensive guide will help you grasp the concept of credit scores, with a special focus on CIBIL scores, and offer practical tips on how to improve and maintain a healthy score.
Table of Contents
What is a credit score?
A credit score is a numerical expression that represents an individual’s creditworthiness. It is based on a detailed analysis of a person’s credit files, sourced from credit bureaus. Credit scores range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better credit health.

What is a CIBIL score?
In India, the most commonly referenced credit score is the CIBIL score, provided by the Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited (CIBIL). The CIBIL score ranges from 300 to 900, with 900 being the highest score possible. A high CIBIL score indicates a strong credit history, making it easier to secure loans and credit at favorable terms.
Why is Your Credit Score Important?
Your credit score affects various aspects of your financial life.
- Loan Approvals: Lenders use credit scores to evaluate the risk of lending money. A higher score increases your chances of getting approved for loans and credit cards.
- Interest Rates: Better credit scores often lead to lower interest rates on loans and credit cards, saving you money in the long run.
- Employment Opportunities: Some employers check credit scores as part of the hiring process, especially for roles that require financial responsibility.
- Renting Property: Landlords may use credit scores to assess the reliability of potential tenants.
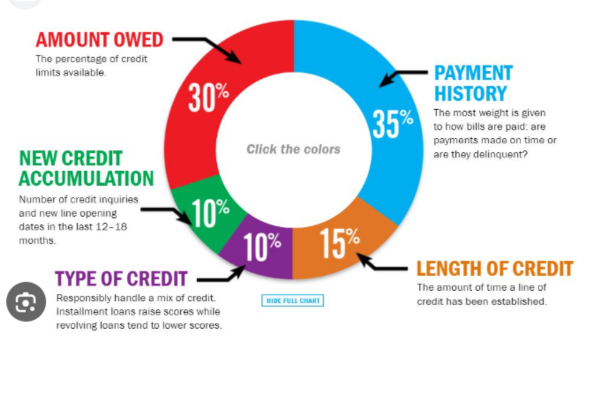
Components of a Credit Score
Several factors contribute to your credit score:
- Payment History (35%): Timely payments on loans and credit cards positively impact your score.
- Amounts Owed (30%): The total amount of debt you owe affects your score. High balances relative to your credit limit can lower your score.
- Length of Credit History (15%): A longer credit history generally boosts your score, as it shows your experience with managing credit.
- New Credit (10%): Frequent applications for new credit can be seen as risky behavior and may lower your score.
- Credit Mix (10%): A diverse mix of credit types (e.g., credit cards, mortgages, personal loans) can positively impact your score.
How to Check Your CIBIL Score
Regularly checking your CIBIL score helps you stay informed about your credit health. Here’s how you can check your CIBIL score:
- Visit the CIBIL website: Go to the official CIBIL website.
- Create an Account: If you don’t have an account, you’ll need to create one.
- Enter personal information: Provide your name, date of birth, and identification details.
- Verification: Complete the verification process.
- Access Your Score: Once verified, you can access your CIBIL score and report.
Why Regularly Check Your CIBIL Score?
- Identify Errors: Monitoring your CIBIL score can help you spot and correct any errors in your credit report.
- Detect Fraud: Regular checks can alert you to fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized credit applications.
- Track Progress: Tracking your score helps you measure the impact of your financial behavior and make necessary adjustments.
How to Improve Your CIBIL Score
Improving your CIBIL score takes time and disciplined financial habits. Here are some effective strategies to boost your score:

1. Make Timely Payments
Consistently paying your bills on time is crucial. This includes credit card bills, loan EMIs, and other recurring payments. Setting up automatic payments or reminders can help ensure you never miss a due date.
2. Reduce Outstanding Debt
Paying down existing debt can significantly improve your credit score. Focus on high-interest debts first, and consider the snowball method—paying off the smallest debts first to gain momentum.
3. Avoid High Credit Utilization
Aim to use less than 30% of your available credit limit. High credit utilization can negatively impact your score. If possible, pay off your balance in full each month.
4. Limit New Credit Applications
Applying for multiple credit accounts in a short period of time can lower your score. Each application results in a hard inquiry, which can temporarily decrease your score. Be selective and apply only when necessary.
5. Keep Old Accounts Open
The length of your credit history affects your score, so keeping older accounts open can be beneficial. Closing old accounts reduces your average account age and available credit, which can lower your score.
6. Monitor Your Credit Report
Regularly review your credit report for inaccuracies. Dispute any errors with the credit bureau to ensure your report reflects accurate information.
7. Diversify Your Credit Portfolio
Having a mix of credit types, such as credit cards, mortgages, and personal loans, can positively impact your score. This shows lenders that you can manage different types of credit responsibly.
Common Myths About Credit Scores
There are several misconceptions about credit scores. Let’s debunk a few
1. Checking Your Own Credit Score Lowers It
Checking your own credit score, known as a soft inquiry, does not affect your score. It’s a responsible financial practice.
2. Closing Credit Cards Will Improve Your Score
Closing a credit card can actually lower your score by reducing your available credit and shortening your credit history. It’s often better to keep the account open, even if you don’t use it frequently.
3. You Only Have One Credit Score
You have multiple credit scores from different credit bureaus, and they may vary slightly. Different lenders may use different scores to assess your creditworthiness.
4. Debt Settlement Improves Your Score
While settling debt may help you manage finances, it typically does not improve your credit score. In fact, it can negatively impact it as it suggests you were unable to pay the full amount owed.
The Bottom Line
Understanding and managing your credit score, especially your CIBIL score, is vital for financial health. By practicing responsible financial habits such as making timely payments, reducing debt, and monitoring your credit report, you can improve and maintain a strong credit score. Remember, improving your credit score is a gradual process, but with dedication and persistence, you can achieve your financial goals.
References
https://www.investopedia.com/how-to-improve-your-credit-score-4590097
https://bettermoneyhabits.bankofamerica.com/en/credit/how-to-improve-your-credit-score


Hi!
newsreporter360.com, Your consistency and kindness in this space don’t go unnoticed.
I recently published my ebooks and training videos on
https://www.hotelreceptionisttraining.com/
They feel like a rare find for anyone interested in hospitality management studies. These ebooks and videos have already been welcomed and found very useful by students in Russia, the USA, France, the UK, Australia, Spain, and Vietnam—helping learners and professionals strengthen their real hotel reception skills. I believe visitors and readers here might also find them practical and inspiring.
Unlike many resources that stay only on theory, this ebook and training video set is closely connected to today’s hotel business. It comes with full step-by-step training videos that guide learners through real front desk guest service situations—showing exactly how to welcome, assist, and serve hotel guests in a professional way. That’s what makes these materials special: they combine academic knowledge with real practice.
With respect to the owners of newsreporter360.com who keep this platform alive, I kindly ask to share this small contribution. For readers and visitors, these skills and interview tips can truly help anyone interested in becoming a hotel receptionist prepare with confidence and secure a good job at hotels and resorts worldwide. If found suitable, I’d be grateful for it to remain here so it can reach those who need it.
Why These Ebooks and Training Videos Are Special
They uniquely combine academic pathways such as a bachelor’s degree in hospitality management or a master’s degree in hospitality management with very practical guidance on the duties of a front desk agent. They also cover the hotel front desk receptionist job description, and detailed hotel front desk duties and responsibilities.
The materials go further by explaining the hotel reservation process, check-in and check-out procedures, guest relations, and dealing with guest complaints—covering nearly every situation that arises in the daily business of a front office operation.
Beyond theory, my ebooks and training videos connect the academic side of hospitality management studies with the real-life practice of hotel front desk duties and responsibilities.
– For students and readers: they bridge classroom study with career preparation, showing how hotel management certificate programs link directly to front desk skills.
– For professionals and community visitors: they support career growth through interview tips for receptionist, with step-by-step questions to ask a receptionist in an interview. There’s also guidance on writing a strong receptionist job description for resume.
As someone who has taught hospitality management programs for nearly 30 years, I rarely see materials that balance the academic foundation with the day-to-day job description of front desk receptionist in hotel so effectively. This training not only teaches but also simulates real hotel reception challenges—making it as close to on-the-job learning as possible, while still providing structured guidance.
I hope the owners of newsreporter360.com, and the readers/visitors of newsreporter360.com, will support my ebooks and training videos so more people can access the information and gain the essential skills needed to become a professional hotel receptionist in any hotel or resort worldwide.
Either way, thank you, newsreporter360.com, for maintaining such a respectful space online.